Published: March 22,2016
After tying the record for the strongest El Niño, as defined by a three-month running mean sea-surface temperature anomaly in the so-called Niño 3.4 region of the central and eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean, sea-surface temperatures are steadily cooling.
(MORE: El Niño 2015-2016 Ties a Record)
Weekly sea-surface temperature (SST) anomalies, which peaked Nov. 18 at 3.1 degrees Celsius above average, have now dropped to 1.7 degrees above average as of March 16, values last seen in late July, according to NOAA's Climate Prediction Center.
You can see this in recent SST animations, illustrating nicely the peak coverage of large warm anomalies during the northern hemisphere's late fall and early winter, followed by a steady decline of the largest anomalies later in February and March.
 Weekly
sea-surface temperature anomalies from late December 2015 through
mid-March 2016. Equatorial Pacific warm anomalies indicative of the
strong El Niño of 2015-2016 is highlighted by the red box.
Weekly
sea-surface temperature anomalies from late December 2015 through
mid-March 2016. Equatorial Pacific warm anomalies indicative of the
strong El Niño of 2015-2016 is highlighted by the red box.Looking below the surface, you can also see a trend of colder-than-average water working its way eastward across the International Date Line, eating away at the warmer-than-average equatorial Pacific water from below, another sign of El Niño's weakening.
 Tropical Pacific temperature anomalies from the surface to a depth of about 450 meters from Jan. 13 through Mar. 14, 2016.
Tropical Pacific temperature anomalies from the surface to a depth of about 450 meters from Jan. 13 through Mar. 14, 2016.NOAA's March El Niño outlook suggests this El Niño may be all but gone by late spring and early summer.
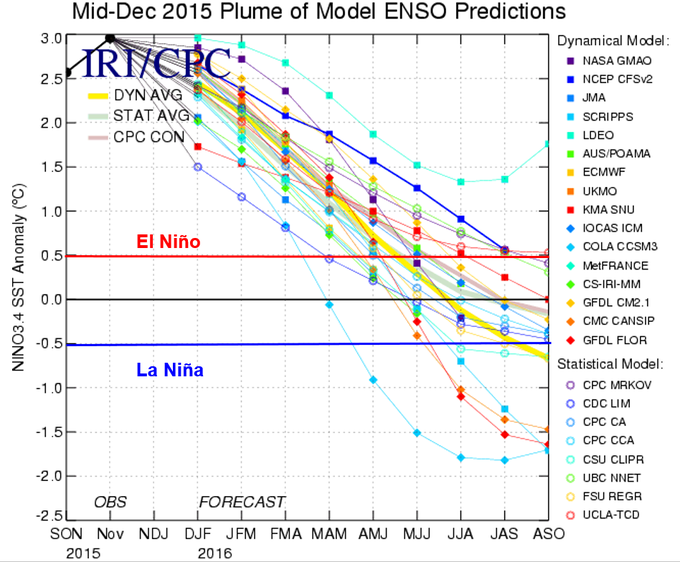
In fact, the majority of model forecasts suggest the equatorial waters may become cooler than average this summer, potentially even swinging into La Niña as early as this fall.
 ENSO plume forecasts in mid-March 2016.
ENSO plume forecasts in mid-March 2016.El Niño and La Niña events typically only last for 9-12 months, and typically recur again every 2-7 years, according to Columbia University's International Research Institute for Climate and Society.
Flip-flops from a strong El Niño to La Niña are not unusual.
Following the record strong El Niño of 1997-98, La Niña almost immediately set in the following summer, reaching moderate-to-strong intensity before finally ending in spring 2001.
A similar thing happened following the strong El Niño of 1972-73.
However, neutral conditions followed three other strong El Niños of 1982-83, 1965-66 and 1957-58.
What Does It All Mean?
Summer 2016
There are some broad trends that have shown up in past weakening El Niño events that could give a hint on what to expect this summer.(MORE: Summer Outlook 2016)
"If we look at rapidly decaying historical ENSO events (trends, instead of actual values), we see that the summer heat is centered in the northern Plains into the Great Lakes states," said Dr. Todd Crawford, chief meteorologist at The Weather Company's energy division.
 A summer 2016 temperature outlook, issued in mid-March 2016, by The Weather Company Professional Division.
A summer 2016 temperature outlook, issued in mid-March 2016, by The Weather Company Professional Division.Atlantic Hurricane Season 2016
As we wrote in early January, strengthening El Niños during the Atlantic hurricane season tend to yield stronger wind shear, which tends to either tear apart developing or mature tropical cyclones.Sure enough, June through October 2015 Caribbean wind shear was the highest on record dating to 1979, according to Dr. Phil Klotzbach, tropical scientist at Colorado State University.
Klotzbach also found that the chance of a U.S. hurricane impact rises dramatically in a La Niña or neutral (neither El Niño or La Niña) season compared to an El Niño season.
Over twice as many hurricanes impact the United States in La Nina years vs. El Nino years. #ElNino
If El Niño was the only factor, that is.
The odds may shift a bit toward a more active Atlantic hurricane season in 2016, but El Niño's absence doesn't guarantee that outcome.
Nor does it mean it poses any greater threat to the U.S. compared to any other year, as landfalls tend to be poorly correlated with numbers of named storms.
Winter 2016-2017
We've said many times an El Niño, La Niña, or the lack of either, known as the neutral phase, is only one large-scale forcing on the atmosphere. It is not the be-all and end-all determining whether a season is wet, dry, cold or warm.Despite that, the peak atmospheric reponse to the equatorial Pacific anomalies tends to occur in the northern hemisphere winter months.
So, in the event we have a La Niña settling in by fall or winter, let's take a look at December-February U.S. temperature and precipitation anomalies during weak (SST anomalies from 0.5 to 0.9 degrees below average), moderate (1.0 to 1.4 degrees below average) and strong (1.5 degrees below average or cooler) La Niñas.
Temperatures
While there are some differences among La Niña magnitudes, some commonalities emerge regarding La Niña winter forcing in the U.S.:
- Cold: Northern Plains, Upper Midwest, New England, New York state, West Coast
- Warm: Southern Plains, Southeast
 December-February
temperature anomalies (degrees Fahrenheit) during 11 weak, 6 moderate,
and 3 strong La Niña events dating to 1950, using the classification
scheme from Jan Null.
December-February
temperature anomalies (degrees Fahrenheit) during 11 weak, 6 moderate,
and 3 strong La Niña events dating to 1950, using the classification
scheme from Jan Null.Precipitation
Again, despite some differences among La Niña magnitudes, some commonalities are apparent:
- Wet: Pacific Northwest, Biterroots (western Montana/Idaho), parts of the Ohio Valley, Tennessee Valley
- Dry: Southern Plains, Gulf/Southeast coast including Florida, Southern California, Desert Southwest
 December-February
precipitation anomalies (inches) during 11 weak, 6 moderate, and 3
strong La Niña events dating to 1950, using the classification scheme
from Jan Null.
December-February
precipitation anomalies (inches) during 11 weak, 6 moderate, and 3
strong La Niña events dating to 1950, using the classification scheme
from Jan Null.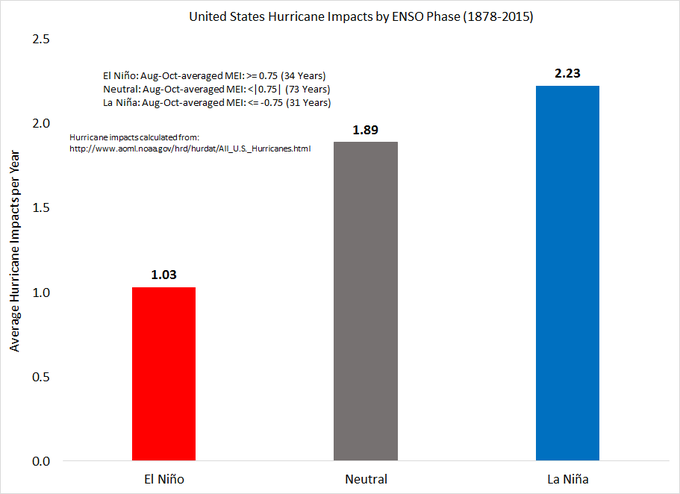

No comments:
Post a Comment